Calculates neutron scattering profiles of proteins from input structures.
The Xtal2sas module is accessible from the Retired section of the main menu.
The purpose of the module is calculate neutron scattering profiles from a user supplied structure file. It is configured to handle trajectory input files (DCD or PDB).
Module calculates neutron scattering profiles for proteins.
The default input file format is DCD. For large numbers of frames we recommend saving your data in the DCD format (~seven fold smaller file size).
The program does not deterine if the input parameters are adequate to converge the scattering profile over the desired range of q. This is the responsbilitiy of the user.
Even if only one structure is to be used to calculate a theoretical scttering curve, it still needs a reference structure even if the coordinates are in a PDB file.
More data points may not be mathematically justified. For SAS there is limited information content related to the size of the molecule measured in the experimental scattering data. 15 to 31 points are generally used. See BIOISIS for a theoretical and pratical reasoning regarding the number of points one should use.
The number of q-points, range of q, and the spacing of the q-points used to create interpolated data files MUST match the input settings that you use in this module to calculate SANS profiles if you wish to compare theoretical and experimental data (Chi-Square Filter).
The final range of q will be from 0 to a maximum q-value of (number of q-values - 1) * delta q, where delta q is the spacing between adjacent q-values entered by the user.
The calculated SANS profiles can be extracted using Extract Utilities or combined from multiple runs using Merge Utilities.
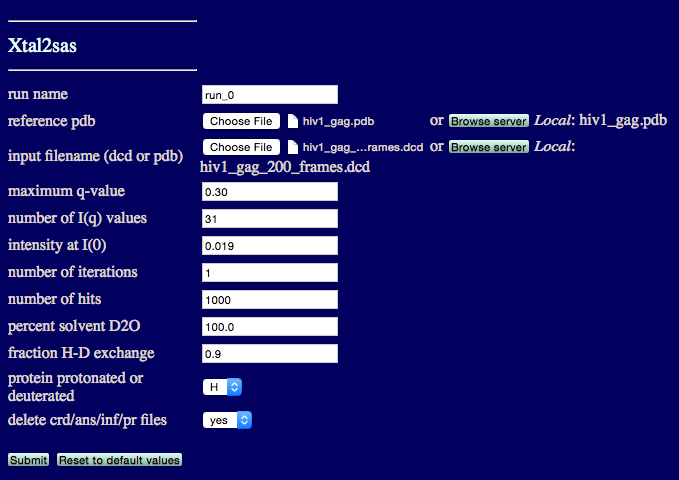
This example calcualtes SANS profiles of a trajectory of 200 structures of the hiv1_gag protein.

run name: user defined name of folder that will contain the results.
reference pdb: PDB file with naming information for coordinates that will be extracted
input filename (dcd or pdb): DCD or PDB file with coordinates that will be used to calculate scattering profile(s).
maximum q value: The maximum value to calculate I(q).
number of I(q) values: The number of individual q-points, including I(0).
intensity at I(0): Experimentally determined value of scattering intensity at q = 0.
number of interations: Number of Monte Carlo iterations. Usually one iteration is adequate.
number of hits: Number of random points that will fill the volume occupied by the molecule.
percent solvent D2O: Solvent compostion, enter a value between 0 and 100.
fraction H-D exchange: Estimate the fraction of hydrogens that exchange with deuterium in the solvent.
protein protonated or deuterated: Pick an option to indicate the deuteration state of the protein.
delete crd/ans/inf/pr files: Option to delete additional files created for each structure.
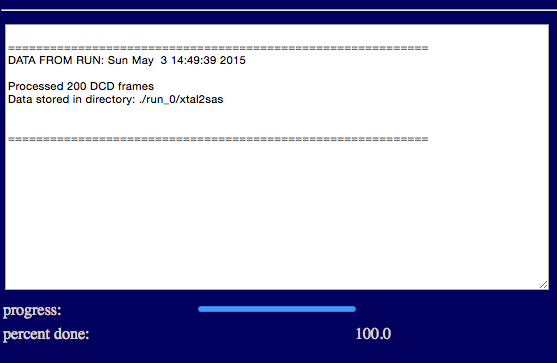
The output will indicate the number of processed frames and the location of the scattering profiles.
Results will be written to a new directory within the given "run name". For example, in the figure it is noted that the structures and dimensions were saved files within the current project directory within the chosen "run name" directory:
./run_0/xtal2sas/
None
input files
output files
scattering profiles are provided as a compressed archive
Module can only calculate neutron scattering of proteins.
Comparison of the crystal and solution structures of calmodulin and troponin C D. B. Heirdon, J. Trewhella, Biochemistry. 27, 909-915 (1988). BIBTeX, EndNote, Plain Text
Determination of the conformations of cAMP receptor protein and its T127L,S128A mutant with and without cAMP from small angle neutron scattering measurements S. Krueger, I. Gorshkova, J. Brown, J. Hoskins, K. H. McKenney, F. P. Schwarz, J. Biol. Chem. 273, 20001-20006 (1998). BIBTeX, EndNote, Plain Text
SASSIE: A program to study intrinsically disordered biological molecules and macromolecular ensembles using experimental scattering restraints J. E. Curtis, S. Raghunandan, H. Nanda, S. Krueger, Comp. Phys. Comm. 183, 382-389 (2012). BIBTeX, EndNote, Plain Text